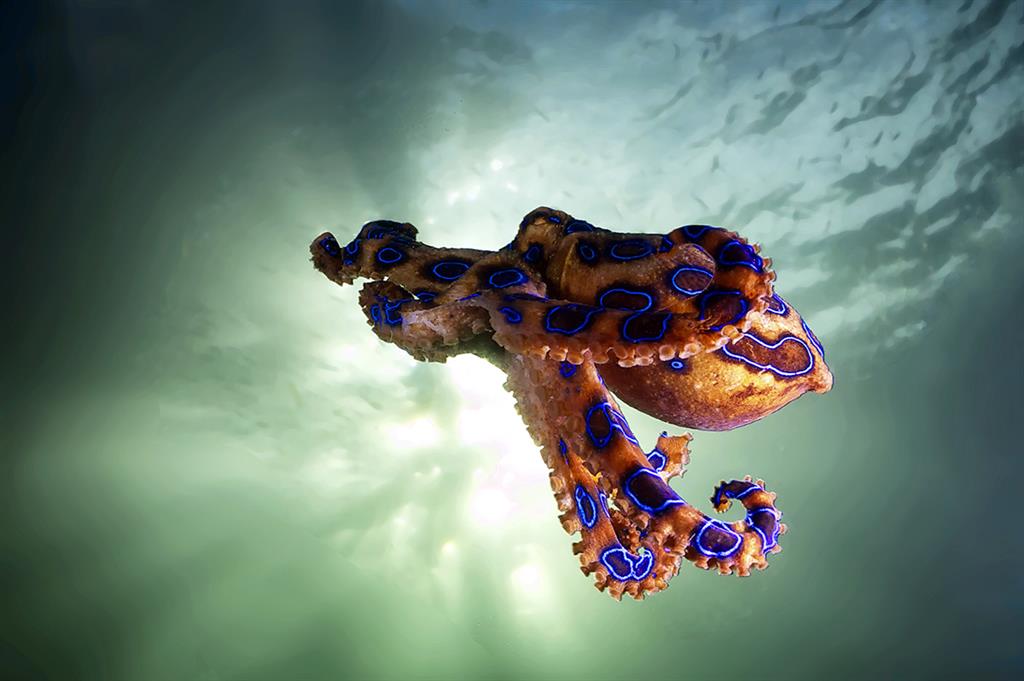
Blue ringed octopus and cone shell bites
FIRST AID FACT SHEET
How to treat blue ringed octopus and cone shell bites
Blue Ringed Octopus are commonly found in tidal pools, and if handled may inflict a potentially fatal bite. This may not be painful, as venom is not always injected (envenomation).
The Cone Shell is mainly found in tropical waters, envenomation happens when they are handled or stepped on and they fire a dart-like barb which delivers venom.
Although different, venoms from both these creatures can cause paralysis and death from respiratory failure within 30 minutes.
What to do
- Follow DRSABCD St John Action Plan
- Urgent medical aid. Call Triple Zero (000) for an ambulance
- Calm casualty and keep them still
- If the bite is on a limb apply a firm broad crepe or elasticised roller bandage starting just above the fingers or toes, and moving upwards on the bitten limb as far as can be reached and immobilise the limb with a splint
- Monitor casualty closely for signs of adverse reactions or deterioration
- Prepare to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if necessary.
Signs and symptoms
- A painless bite with a spot of blood visible.
- Numbness to lips and tongue, muscle weakness of respiration which can stop the casualties breathing.
Caused by
- Handling the creature
- Accidentally standing on the creature.